The Process and Uses of Aluminum Profile Radiators
1. The Manufacturing Process of Aluminum Profile Radiators
1.1. Material Selection
The production of aluminum profile radiators starts with the careful selection of high-quality aluminum alloys. Aluminum,
being a lightweight and highly conductive metal, ensures efficient heat transfer while maintaining structural integrity.

1.2. Extrusion
The most common method for manufacturing aluminum profiles is extrusion. In this process,
the selected aluminum alloy is heated and forced through a shaped die to create the profile.
The extruded profiles are then cooled and cut into appropriate lengths.

1.3. Finishing and Coating
To enhance the aesthetic appeal and protect against corrosion, the aluminum profiles undergo surface finishing processes.
Anodizing, powder coating, or painting are commonly employed methods to achieve a durable and visually pleasing finish.

1.4. Assembly
Once the individual aluminum profiles are ready, they are assembled into the final structure.
The assembly process may involve various methods such as welding, mechanical fixing,
or gluing, depending on the profile's design and application.

2. Uses of Aluminum Profile Radiators
2.1. Residential Heating Systems
Aluminum profile radiators find widespread use in residential heating systems due to their excellent heat conduction and lightweight nature.
They efficiently heat up and distribute warmth throughout the space, offering cost-effective and eco-friendly heating solutions.

2.2. Automotive Industry
In the automotive sector, aluminum heat sink profile are commonly used in engine cooling systems.
The lightweight construction helps improve fuel efficiency,
and the high thermal conductivity ensures effective heat dissipation, preventing engine overheating.
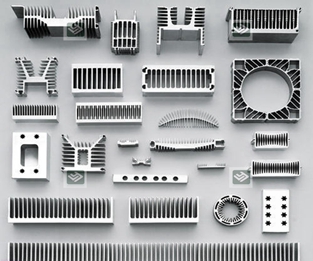
2.3. Industrial Cooling Applications
Industries often utilize aluminum heat sink for cooling applications, such as cooling of electronic components, power electronics, and machinery.
The excellent heat transfer capabilities of aluminum make it ideal for efficiently dissipating heat from high-power systems.

2.4. Solar Thermal Systems
In solar thermal systems, aluminum heat sink play a crucial role in absorbing and transferring solar energy to heat water or air.
The lightweight nature of aluminum makes these radiators suitable for rooftop installations and various solar applications.

2.5. Architectural and Inside-house Design
Aluminum heat sink is favored by architects and interior designers for their sleek and modern appearance.
They are used as decorative elements and heating solutions in commercial buildings, hotels, and other public spaces.

Conclusion
Aluminum heat sink is a testament to the versatility and efficiency of aluminum as a material. The manufacturing process,
starting from material selection to assembly, ensures that these heat sink meet the highest standards of performance and reliability.
Their broad range of applications, spanning from residential heating to automotive and industrial cooling,
show their indispensable role in modern-day heating and cooling systems. As technology advances and design trends evolve,
aluminum profile radiators are expected to continue playing a significant part in shaping the future of thermal management solutions.

